Can you name the main components running inside Cloud Foundry? Do you know what each of them does?
Main components are:
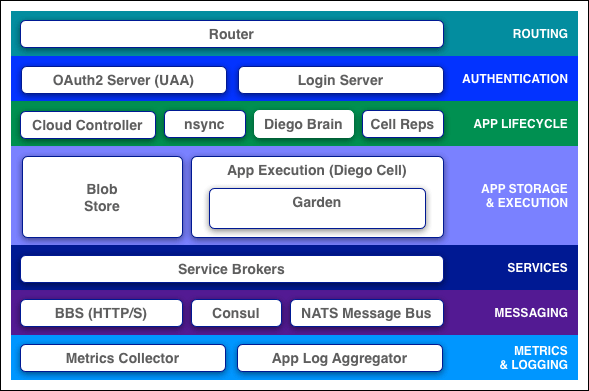
Router: routes incoming traffic to cloud controller or the hosted application in diego cell. It periodically queries the Diego bulletin board system to determine which cells and containers each application currently runs on. Using this router recomputes new routing table based on IP addresses of each cell VM and the host side port number for the cell's container.
Oauth2 Server(UAA) and Login server work together to provide the identity management.
Cloud controller and Diego brain: CC is responsible for application life-cycle and deployment. It directs the diego brain through CC Bridge component to coordinate individual Diego cells to stage and run applications.
CC also maintains record of orgs, spaces, user roles and services.
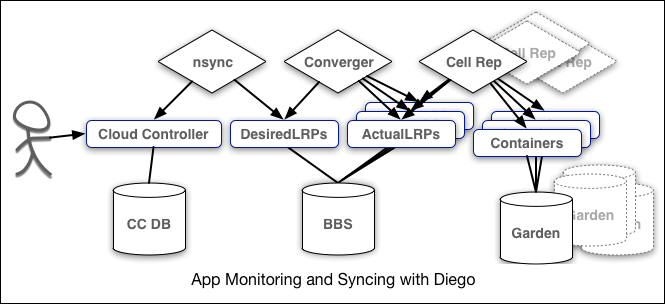
nsync: recieves the message from CC when user scales an app. It writes number of instances into a desiredLRP structure in the Diego BBS database.
BBS: uses its convergence process to monitor desiredLRP and actualLRP values. It is responsible for launching and killing the application instances.
cell reps: monitors the containers and provides the ActualLRP value.
Blobstore: is a repository of large binary files i.e. application code packages, buildpacks, droplets.
Diego cell: It is a VM on which application instances, tasks i.e. application or staging, all run as Garden containers. Cell reps container manages the lifecycle of garden containers and the process running in them, and reports their status to the BBS and emits their logs and metrics to Loggregator.
Service broker: is responsible for providing the service instances for provisioned and binded service to the app.
Consul: stores longer lived control data i.e. component ip addresses and distributed locks which prevents components from duplicating actions.
BBS: stores more frequently updated and disposable data such as cell and application status, unallocated work and heartbeat messages. BBS uses MySQL server to save data.
NATS: lightweight messaging and queuing protocol developed using Ruby is used by router-emitter to broadcast the latest routing tables to the router.
Loggregator: streams application logs to developers.
Metrics Collector: gathers metrics and statistics from the components. Operators can use this information to monitor a Cloud Foundry deployment.
What does Diego refer to?
Cloud Foundry uses the Diego architecture to manage application containers. Diego components assume application scheduling and management responsibility from the Cloud Controller.
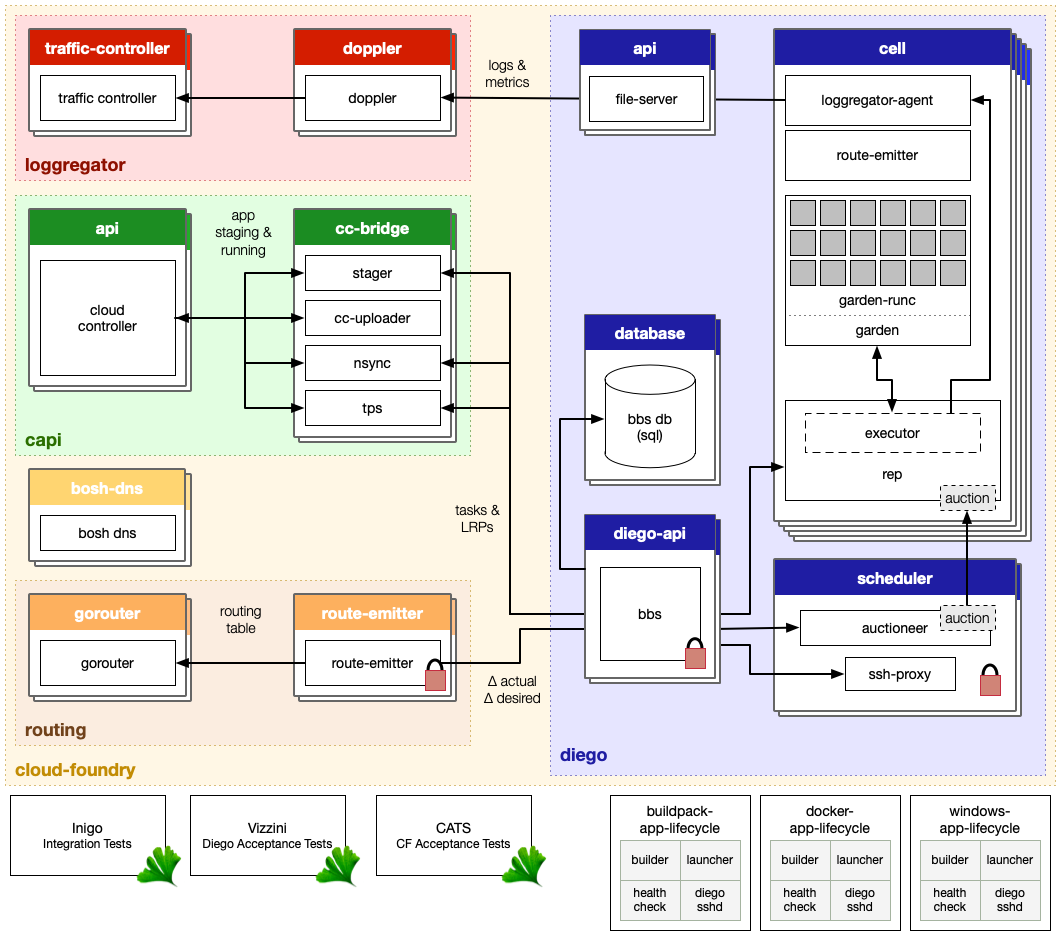
Refer to CF section diego-architecture.
What is Garden?
It's the Cloud Foundry container back end, which became available in Diego—the current Cloud Foundry runtime. It is used to create and manage isolated environments called containers. It provides a platform-independent server and clients to manage Garden containers. Garden has pluggable backends for different platforms and runtimes, and specifies a set of interfaces that each platform-specific backend must implement. At the moment, three back ends are available: Linux, runC (a container specification from the Open Container Initiative), and Windows.
What components run in a Diego Cell?
1. Diego brain: It consists of auctioneer. Responsible for distributing tasks and LRP to diego cells.
2. Diego Cells: manage and maintain tasks and LRP's. Each cell consists of 4 other component i.e. Reps, executor, garden and metron agent
3. Diego Bulletin Board System: is a DB for diego cell to maintain task and LRP related data.
4. Access VM i.e. file server (blobstore) and ssh proxy i.e. broker connections between ssh client and servers.
5. Consul: provides dynamic service registration and load balancing through DNS resolution. Also provides a consistent key-value store for maintenance of distributed locks and component presence.
What is the System domain? And the application domain?
are full domain you want associated with applications pushed to your Cloud Foundry installation, for example
'domain' is used by all CF components (UAA, Login, CC). 'system_domain' is used by cloud controller only for initialization step. This is the domain that is used by 'system_domain_organization' for "system" apps like the console.
What is Cloud Foundry’s API endpoint for?
The API endpoint, or target URL, for your Cloud Foundry instance is the URL of the Cloud Controller.
'cf api'
What is a container? What is it used for?
What is a droplet? How is it created? Where is it stored?
An archive within Cloud Foundry that contains the application ready to run on Diego. A droplet is the result of the application staging process(The staging Task downloads buildpacks and the app’s buildpack cache, if present. It then uses the buildpack that is detected automatically or specified with the
What are the purposes of the two data stores used by the Cloud Controller?
CC_DB and Blobstore are two data stores used by CC.
CC_DB stores data for orgs, spaces, services, user roles, and more.
Blobstore is used to store large binaries i.e. application packages, buildpacks, droplets, buildpack cache, and resource cache.
Main components are:

Router: routes incoming traffic to cloud controller or the hosted application in diego cell. It periodically queries the Diego bulletin board system to determine which cells and containers each application currently runs on. Using this router recomputes new routing table based on IP addresses of each cell VM and the host side port number for the cell's container.
Oauth2 Server(UAA) and Login server work together to provide the identity management.
Cloud controller and Diego brain: CC is responsible for application life-cycle and deployment. It directs the diego brain through CC Bridge component to coordinate individual Diego cells to stage and run applications.
CC also maintains record of orgs, spaces, user roles and services.
nsync: recieves the message from CC when user scales an app. It writes number of instances into a desiredLRP structure in the Diego BBS database.
BBS: uses its convergence process to monitor desiredLRP and actualLRP values. It is responsible for launching and killing the application instances.
cell reps: monitors the containers and provides the ActualLRP value.

Blobstore: is a repository of large binary files i.e. application code packages, buildpacks, droplets.
Diego cell: It is a VM on which application instances, tasks i.e. application or staging, all run as Garden containers. Cell reps container manages the lifecycle of garden containers and the process running in them, and reports their status to the BBS and emits their logs and metrics to Loggregator.
Service broker: is responsible for providing the service instances for provisioned and binded service to the app.
Consul: stores longer lived control data i.e. component ip addresses and distributed locks which prevents components from duplicating actions.
BBS: stores more frequently updated and disposable data such as cell and application status, unallocated work and heartbeat messages. BBS uses MySQL server to save data.
NATS: lightweight messaging and queuing protocol developed using Ruby is used by router-emitter to broadcast the latest routing tables to the router.
Loggregator: streams application logs to developers.
Metrics Collector: gathers metrics and statistics from the components. Operators can use this information to monitor a Cloud Foundry deployment.
What does Diego refer to?
Cloud Foundry uses the Diego architecture to manage application containers. Diego components assume application scheduling and management responsibility from the Cloud Controller.

Refer to CF section diego-architecture.
What is Garden?
It's the Cloud Foundry container back end, which became available in Diego—the current Cloud Foundry runtime. It is used to create and manage isolated environments called containers. It provides a platform-independent server and clients to manage Garden containers. Garden has pluggable backends for different platforms and runtimes, and specifies a set of interfaces that each platform-specific backend must implement. At the moment, three back ends are available: Linux, runC (a container specification from the Open Container Initiative), and Windows.
What components run in a Diego Cell?
1. Diego brain: It consists of auctioneer. Responsible for distributing tasks and LRP to diego cells.
2. Diego Cells: manage and maintain tasks and LRP's. Each cell consists of 4 other component i.e. Reps, executor, garden and metron agent
3. Diego Bulletin Board System: is a DB for diego cell to maintain task and LRP related data.
4. Access VM i.e. file server (blobstore) and ssh proxy i.e. broker connections between ssh client and servers.
5. Consul: provides dynamic service registration and load balancing through DNS resolution. Also provides a consistent key-value store for maintenance of distributed locks and component presence.
What is the System domain? And the application domain?
are full domain you want associated with applications pushed to your Cloud Foundry installation, for example
cloud-09.cf-app.com. 'domain' is used by all CF components (UAA, Login, CC). 'system_domain' is used by cloud controller only for initialization step. This is the domain that is used by 'system_domain_organization' for "system" apps like the console.
When CC boots for the first time it creates first organization (system_domain_organization) and creates the system_domain domain with the system_domain_organization as its owner. If this is not configured, apps will be able to use the same base domain as the CC for their own routes. And this domain may be claimed by any user's organizations, as no one "owns" it.
SYSTEM_DOMAIN, APP_DOMAIN are defined in CF deployment manifest.
The API endpoint, or target URL, for your Cloud Foundry instance is the URL of the Cloud Controller.
'cf api'
What is a container? What is it used for?
Each instance of an app deployed to CF runs within its own self-contained environment, a Garden container. This container isolates processes, memory, and the filesystem using operating system features and the characteristics of the virtual and physical infrastructure where CF is deployed.
CF achieves container isolation by namespacing kernel resources that would otherwise be shared. The intended level of isolation is set to prevent multiple containers that are present on the same host from detecting each other. Every container includes a private root filesystem, which includes a Process ID (PID), namespace, network namespace, and mount namespace.
What is a droplet? How is it created? Where is it stored?
An archive within Cloud Foundry that contains the application ready to run on Diego. A droplet is the result of the application staging process(The staging Task downloads buildpacks and the app’s buildpack cache, if present. It then uses the buildpack that is detected automatically or specified with the
-b flag to compile and stage the application). It is stored in blobstore.What are the purposes of the two data stores used by the Cloud Controller?
CC_DB and Blobstore are two data stores used by CC.
CC_DB stores data for orgs, spaces, services, user roles, and more.
Blobstore is used to store large binaries i.e. application packages, buildpacks, droplets, buildpack cache, and resource cache.
Thanks for sharing an excellent post, which is helped to me. Surely I suggest to this blog for my friends and I got extra knowledge from your post. Keep it up and I like more new posts...
ReplyDeleteLinux Training in Chennai
Linux Course in Chennai
Pega Training in Chennai
Primavera Training in Chennai
Unix Training in Chennai
Embedded System Course Chennai
Linux Training in OMR
Linux Training in Velachery
What a great post it was. I have bookmarked this blog for my future reference. Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteIELTS Coaching in Tambaram
IELTS Coaching Centre in Tambaram
IELTS Training in Tambaram
IELTS Coaching In Velachery
IELTS Coaching Centre in Velachery
IELTS Training in Velachery
IELTS Coaching in T Nagar
IELTS Classes in T Nagar
IELTS Training in T Nagar
Nice idea,keep sharing your ideas with us.i hope this information's will be helpful for the new learners.
ReplyDeleteiOS Training in Chennai
iOS Course in Chennai
JAVA Training in Chennai
Python Training in Chennai
Hadoop Training in Chennai
Android Training in Chennai
IOS Training in Chennai
iOS Training in OMR
The information which you have provided in this blog is really useful to everyone. Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeletePivotal Cloud Foundry Online Training in Ameerpet
Cloud Foundry Training in Hyderabad
PCF Training in Hyderabad
Cloud Foundry Developer Online Training in Hyderabad
It was a great information and Its really worth reading it.
ReplyDeletePivotal Cloud Foundry Online Training
Thanks for sharing such a great information..Its really nice and informative..
ReplyDeletepivotal tutorial
pivotal training
This article will be useful for others who want to know more about technology.Thanks for sharing
ReplyDeletePivotal Cloud Foundry Online Training
Cloud Foundry Training
Cloud Foundry Training in Hyderabad
PCF Training